Share on
- Copy link
The use of cryptocurrency and NFTs are reportedly increasing in African markets, with projections indicating substantial growth.
Last updated Nov 18, 2024 at 08:00 PM
Posted Nov 18, 2024 at 07:00 PM

BitcoinThe second largest continent in the world, Africa, is home to over 1.6 billion people yet technology adoption is still in its early stages. Often, individuals in developed countries are more familiar with technological advancements than those in Africa.
However, cryptocurrencies are not new to Africa. Many of younger Africans have embraced cryptocurrencies as a secondary source of income. Although many people still struggle to understand the technology behind it, the ability it provides for people to sell anything quickly for a profit has made it highly popular.
Similarly, NFTs are widely used, especially in Nigeria, Kenya, Ghana, and South Africa. Despite this, obstacles to NFT implementation in Africa have had an impact on the rate of adoption and usage throughout the continent.
Cryptocurrency is a kind of currency that relies on blockchain technology, an open, distributed ledger for recording transactions. It uses digital files as its medium of exchange. Cryptocurrency files are typically constructed with cryptography techniques. Cryptocurrency uses "decentralized control," which means it is not run by a single person or institution.
Africa does not have a particularly large cryptocurrency market, but it is expanding. South Africa, Nigeria, Zimbabwe, Kenya and Ghana are the top 5 African nations where communities are embracing Bitcoin, according to BitcoinAfrica.io. Additionally, they have the most active local bitcoin networks and the highest levels of demand for virtual money.
As for Africa, the number of users in the Cryptocurrencies market is expected to reach 53.89m users by 2025.
-Statista
Additionally, South Africa, Nigeria, and Kenya are among the top 10 nations in the world in terms of cryptocurrency adoption, according to bitcoin.com. Does that represent how African nations are implementing this modern technology? Nigeria has one of the most active peer-to-peer Bitcoin trading markets in the world, but the nation has so far outlawed cryptocurrencies and warned its people against making investments in them because they lack legal protection.
One of the reasons Africans are switching to cryptocurrencies is the continent's economic unrest. Because businesses like Bitcoin do not have a single domain and their transactions are unaffected by national inflation rates, individuals of African nations can safeguard their income from a faltering economy. In addition, Bitcoin facilitates international payments. Since bitcoin businesses use blockchain technology, which uses a decentralized method to preserve public data, PayPal, for instance, was initially banned in Nigeria due to fraud and money laundering operations.
Because cryptocurrencies are decentralized, transactions are also quick, cheap, and free of middlemen. Finally, they are secure in terms of cryptography. African entrepreneurs frequently aspire to operate their companies on a global level.
Some of these companies began utilizing blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies to stand out in the global market and guard against currency depreciation. Therefore, governments' decision to outlaw cryptocurrencies will not prevent virtual currency transactions from taking place online.
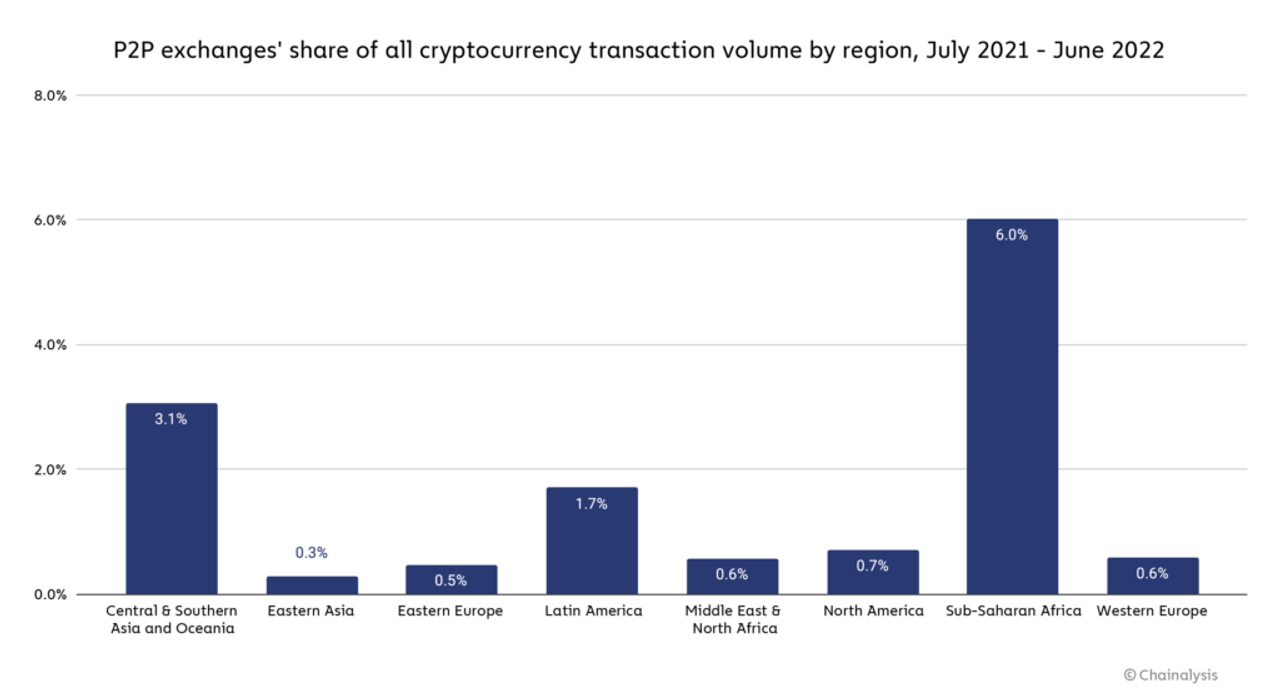
The rapid use of cryptocurrencies by Africans has contributed to the expansion of NFTs on that continent. Africa had the world's fastest adoption rate of cryptocurrencies in 2021, according to research by Chain analysis, with a 1200% growth in usage between July 2020 and June 2021.
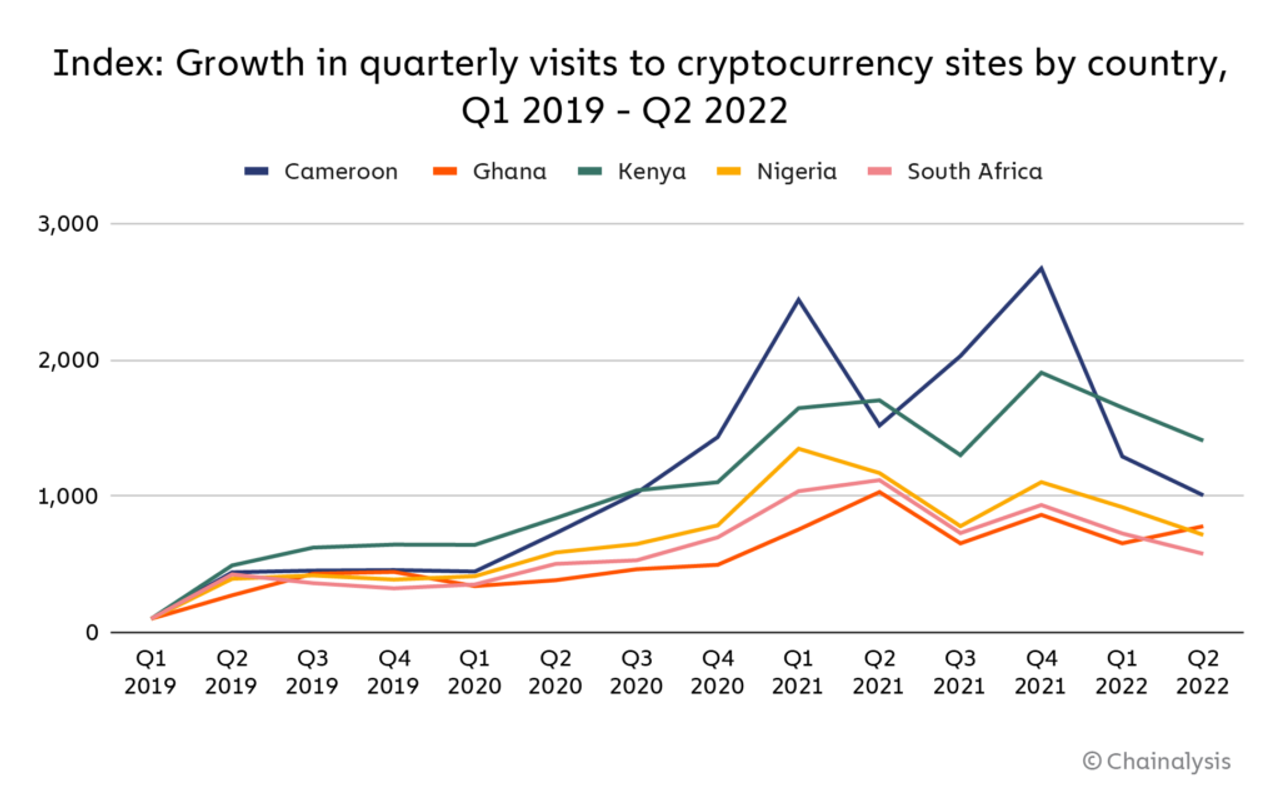
This was around the time that NFTs started to get increasing notoriety. Crypto arts' visibility was successfully raised by Mike Winkelmann's record-breaking NFT sales in December. The prospect of earning up to $69 million from the sale of digital art sparked excitement throughout the world, particularly in Africa. Africa embraced digital art rather later than other continents because many individuals were still unaware of the NFTs' underlying technology and its applications. NFTs trailed behind bitcoin activities, which increased dramatically. The continent, however, caught up after popular NFT collections like the Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC) and experienced rapid price hikes. Although many of those who entered the market did so for speculative reasons, the popularity of NFTs quickly grew among young people who lacked access to jobs or other sources of money. They began trading in the hope of profiting more than they had invested in the NFT within a short period.
Africans are already making more NFT investments than ever before—and not merely to sell them for a profit. As blockchain technology became increasingly widespread in Africa, many individuals saw that everyone could gain from the decentralized economy.
Additionally, it was found that minting NFTs was less complicated than anticipated. Nigeria and South Africa were ranked sixth and twelfth in a recent Finder poll, respectively, for their use of NFTs.
In April 2022, a group of Ghanaian pallbearers who had become internet memes in 2020 reaped the benefits of their fame. The group's leader, Benjamin Aidoo, sold the coffin dance as an NFT for 372 ETH ($1.046 million at the time). The most expensive transaction outside of Africa to date is the NFT sale.
Adisa Olashile, a phone photographer from the neighboring country of Nigeria who mints and sells his works as NFTs, posted pictures of an old drummer that he had captured on Twitter. He claimed he planned to sell the NFT prints and give the seasoned drummer 50% of the sales revenue. The photographer quickly revealed that each shot had been sold for more than one million nairas, or 0.3 ETH, on OpenSea. He then recorded and posted online the drummer's astonishment at being presented with his earnings. The kind deed naturally garnered a lot of attention on social media.
Many individuals applauded the photographer for being so kind, and some people wanted to know how they could also board the NFT train. Since then, as more people have tried to profit from the sector, NFT conversations have sharply expanded on Nigerian social media sites.
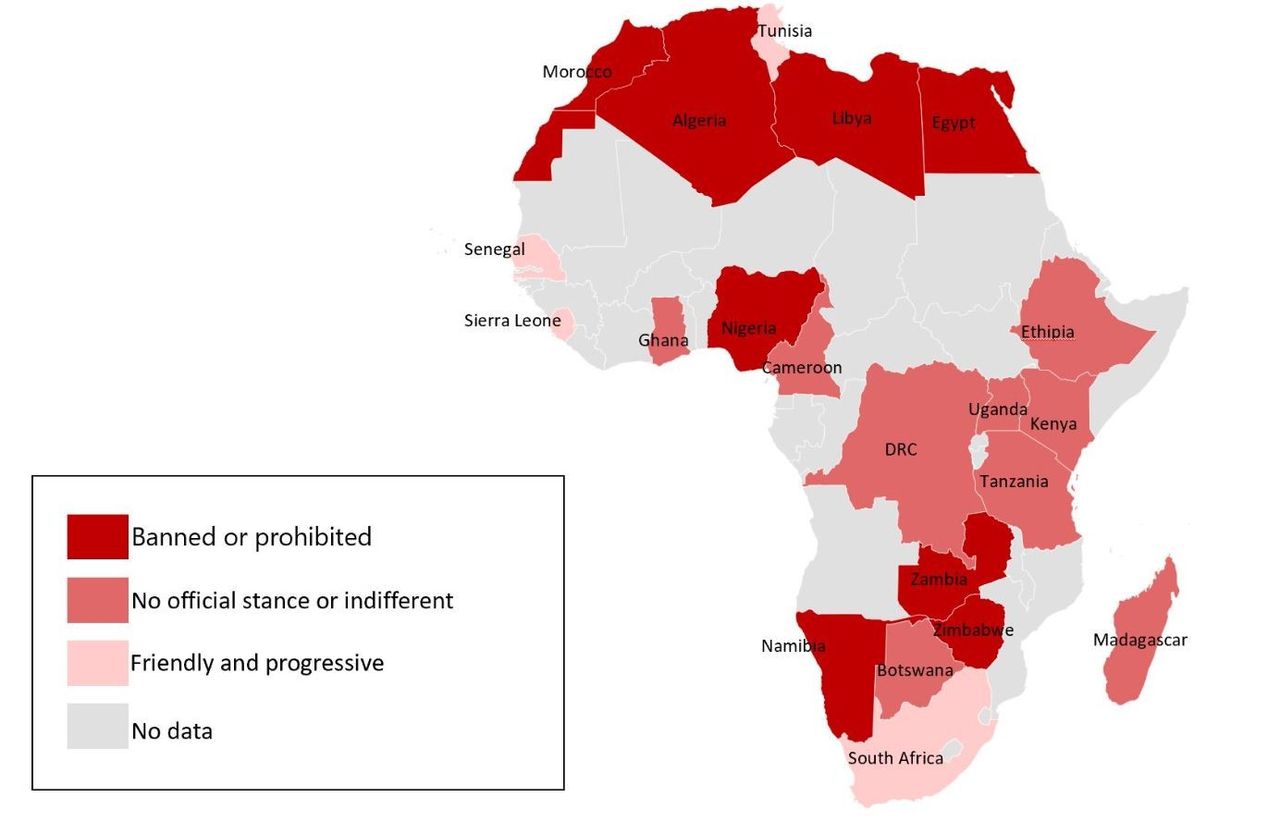
Like many other countries, African countries have not been particularly welcoming of the use of cryptocurrencies inside their borders. Those that haven't put trading restrictions in place have discouraged their citizens from investing in cryptocurrencies. Countries like Algeria, Egypt, Morocco, and Tunisia have total bans on cryptocurrency commerce, whilst others like Nigeria, Cameroon, and Gabon have only minor limitations. The fact that NFTs are traded using the local currency of the blockchain they are hosted on makes it difficult for supporters of NFTs in countries where there are limitations or prohibitions to simply conduct trading. In Nigeria, for instance, financial institutions are prohibited from doing cryptocurrency-related transactions and are compelled to close any accounts based on them. Customers have effectively been encouraged to perform their trading activities on peer-to-peer platforms by this. Official rules have made it difficult for people to use and trade NFTs in Africa, yet the market is nevertheless booming there. In addition to giving African artists a means to sell their works, it has also made it possible for thousands of individuals on the continent to support themselves. NFTs, however, can help the continent in more ways than only by creating opportunities. The adoption of NFTs could greatly improve transparency and authenticate ownership in a region of the world where property ownership is still determined manually. By nature, NFTs are recognizable and traceable. As a result, not only will the status of ownership be preserved, but locating a property owner will also be simple. The initiatives coming out of Africa show that the adoption of NFT will accelerate in the years to come. As time goes on, more initiatives will likely be launched that have the potential to revolutionize Africa and its people.
In conclusion, increasing mobile phone use, financial exclusion, and the promise for more secure and transparent transactions are all contributing to the growth of cryptocurrencies and NFTs in Africa. Adoption, however, also faces obstacles such as a lack of regulation and instruction. Stakeholders must collaborate to build an ecosystem that is inclusive and accessible to all to guarantee the success and sustainability of cryptocurrencies and NFTs in Africa.