Share on
- Copy link
Liquidity Pools (LP) are proving to be a critical technology in the crypto ecosystem. LP in DeFi has been vital as it provides the necessary funds for AMM, Borrowing-Lending Protocols, Gaming, and several other uses.
Last updated Nov 12, 2022 at 03:31 PM
Posted Nov 11, 2022 at 03:23 PM

Among the core applications enhancing the present DeFi space are liquidity pools. They play a key role in automated market makers (AMM), borrowing-lending protocols, yield farming, artificial products, online insurance, gaming, and a long list of other applications.
A liquidity pool is essentially a large electronic stack of resources in a trustless setting that allows users to include money in it.
Decentralized finance (DeFi) has produced an upsurge in network activity. Volumes on DEXs are capable of substantially competing with the turnover on controlled platforms. DeFi protocols have roughly $40 billion Total value locked in them as of November 2022.
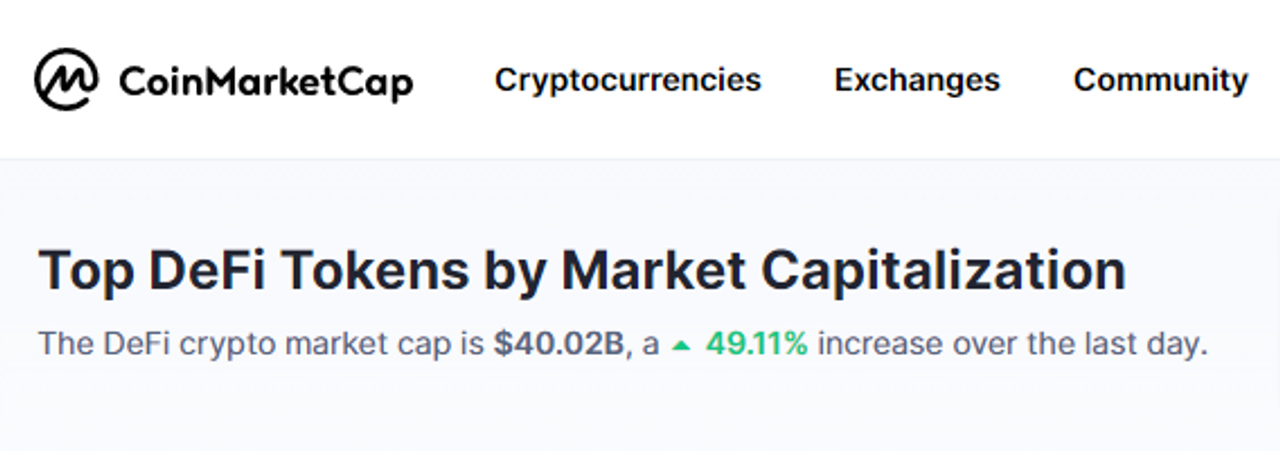
DeFi Market Cap Source: CoinMarketCap
DeFi market cap is growing and future product categories are being introduced to the ecosystem quickly. We will explore the role of LP in DeFi and other sections.
Money that is secured using a smart contract is called a liquidity pool. Decentralized lending and dealing are made possible via liquidity pools, among many other uses that we'll discuss later.
Several decentralized exchanges (DEX), including Uniswap, are founded on liquidity pools. To form a marketplace, individuals known as liquidity providers (LP) merge multiple coins of equivalent worth into a pool. They receive transaction charges from the activities that take place in their pools in accordance with their percentage of the total liquidity in return for contributing their cash.
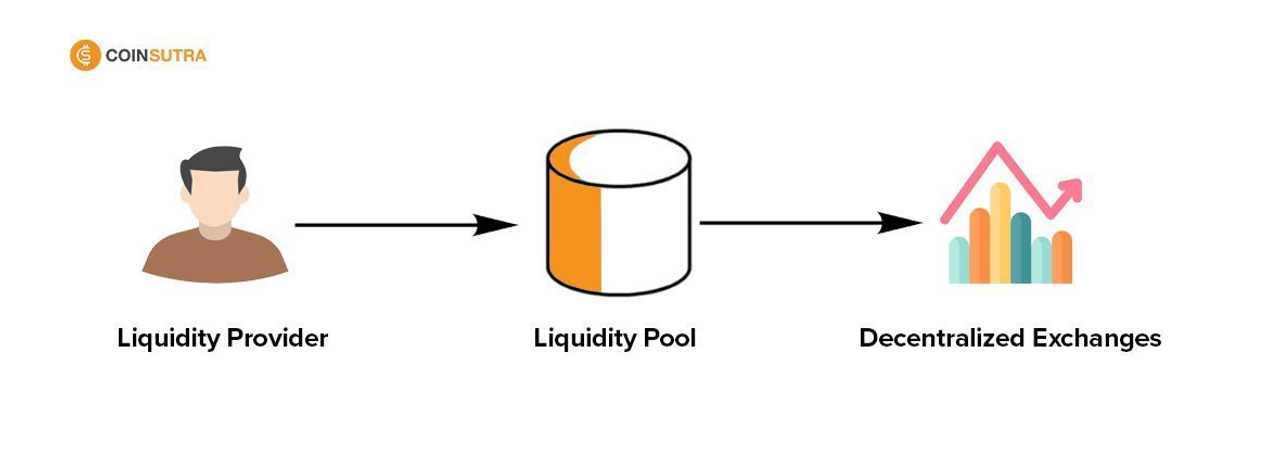
What is liquidity Pool?
Automated Market Makers (AMM) have widened the availability of share trading because anyone can act as a liquidity provider.
The Bancor was the first LP ever developed in the crypto ecosystem. These are the best Liquidity pools (LP) on the Ethereum blockchain:
The best liquidity pools (LP) on the Binance chain are these:
This contest has been altered by automated market makers (AMM). They represent a major technological advancement that enables network trading without an order book. Trading on currency combinations that are anticipated to be very unhedged on order book platforms can be done without a primary intermediary because of this.
An order book marketplace can be compared to P2P, where purchasers and sellers are linked by the order book. For instance, as transactions take place immediately among customer accounts, purchasing on Binance DEX is P2P. Investing with an AMM is unique. Buying on an AMM can be compared to peer-to-contract.
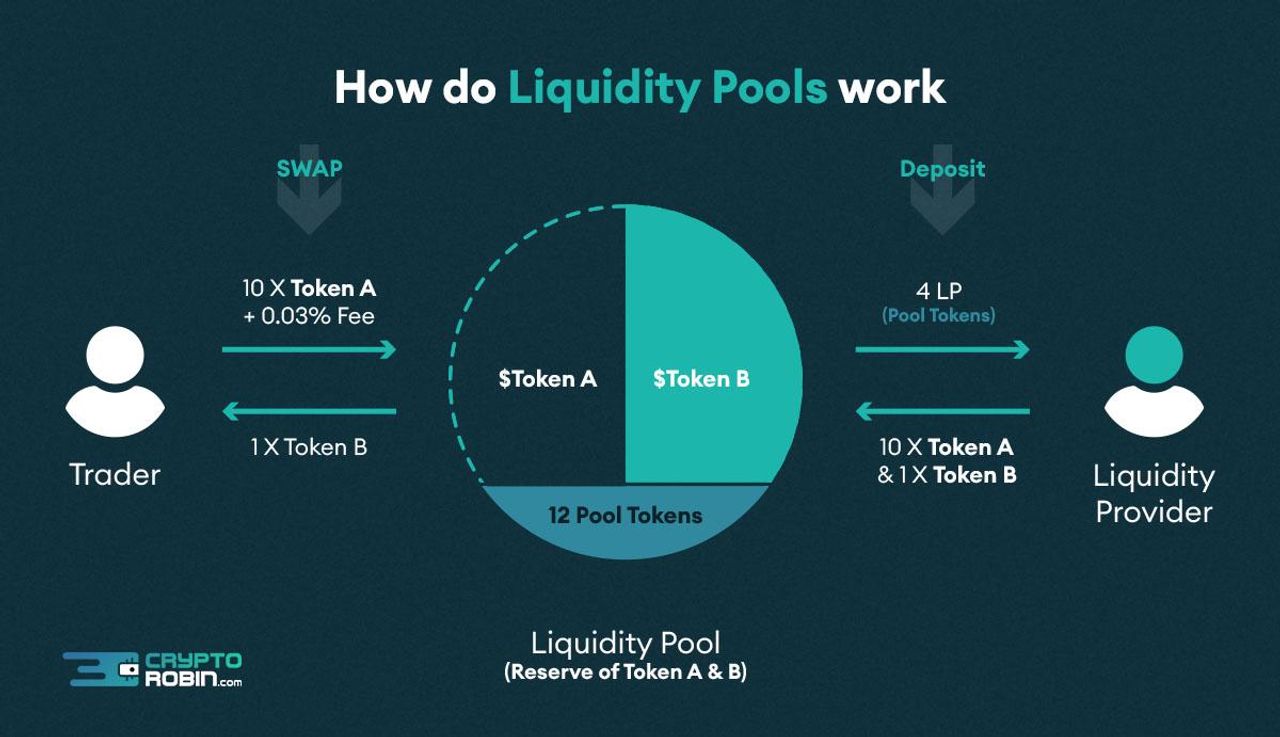
Working of liquidity pools
As previously discussed, a liquidity pool is a collection of money that liquidity suppliers contribute to smart contracts. There is no middleman ordinarily whenever you execute a payment on an AMM. As an alternative, you carry out the transaction using the money in the liquidity pool. There need not be a vendor present for the purchaser to purchase; all that is required is enough liquidity in the pool.
There is no vendor on the opposite end when purchasing the newest food token on Uniswap in the conventional sense. Rather, the mechanism that controls what occurs in the pool controls your action. Additionally, this scheme combines deals that take place in the pool to establish value.
Any person can contribute to the liquidity pool and earn incentives.
Most of our discussion thus far has focused on AMMs, the most widely used application of liquidity pools. But since pooling liquidity is such a fundamentally straightforward idea, it may be applied in a variety of contexts.
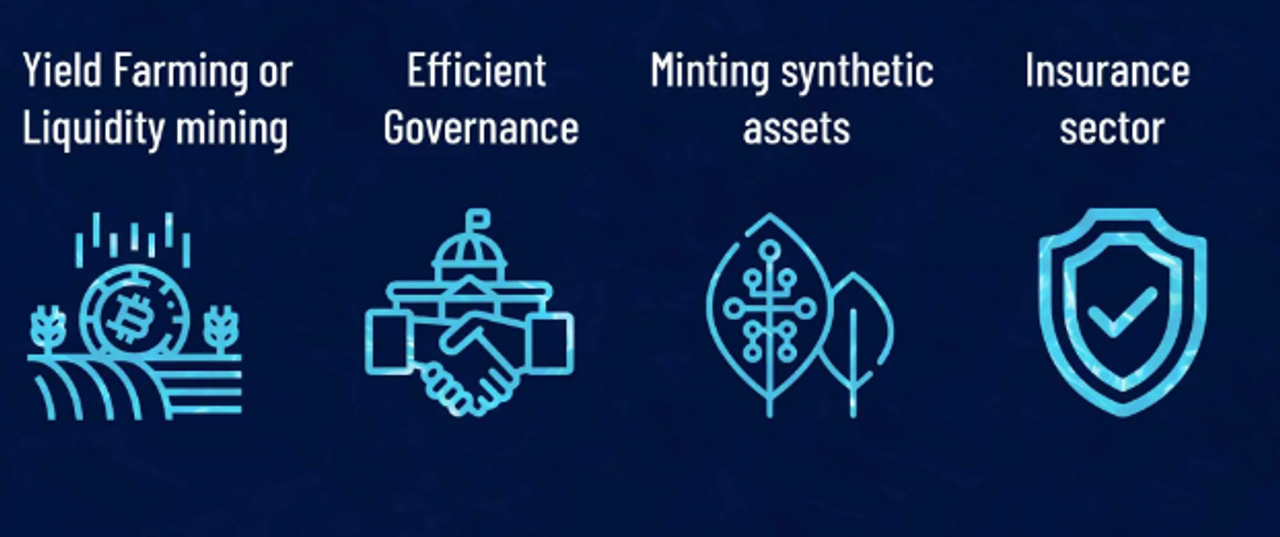
Role of LP in DeFi services
In yield farming, participants contribute funds to liquidity pools, which are the foundation of automatic yield-producer systems like yearn, where the assets are then employed to produce revenue.
For cryptocurrency initiatives, getting additional tokens into the hands of the correct individuals is highly challenging. One popular method is liquidity mining. In essence, customers that deposit their coins into a liquidity pool receive the coins via a program. The freshly created coins are then allocated according to each person's pooling contribution.
The token distribution in the initiatives is automated using LP and smart contracts. This method makes the method token distribution reliable, secure, and transparent.
Sometimes a significant number of token votes are required before a proper governance resolution may be advanced. By pooling the money, users can unite behind a goal they consider crucial to the community.
Tranching seems to be another innovative application of liquidity pools. This idea, which was adapted from conventional banking, calls for categorizing monetary goods according to their risks and rewards. These instruments, as one might anticipate, give LPs the option to choose specific risk and return characteristics.
Insurance of digital and physical items can also be automated using LP. This will bring transparency and make it reliable for the users. Some platforms are already using this technology for insurance.
Liquidity pools are also necessary for the ledger to mint synthetic products. You can create a synthesized coin that is tied to any item by adding some security to a liquidity pool and connecting it to a reliable oracle. The concept is more convoluted, but the fundamental concept is still the same.
Investment strategies that use DeFi (decentralized finance) include staking and liquidity provision. At first glance, neither is superior to the other; the choice relies on your financial plan. Since several initiatives lack a mandatory staking time, staking is a preferable long-term DeFi approach, since you can continue to stake coins forever while still receiving the benefits.

Liquidity Pool vs Staking
Everyone who stakes can profit with a high annual percentage yield (APY). Several initiatives also provide their own coins as incentives. Earning an additional income is the main advantage of staking. When you stake, your coins do the labor for you, allowing you to relax and enjoy yourself.
Offering to fund is a DeFi operation with a high reward/risk ratio. Any time you give AMM funding, there's a chance of sudden breakdown. When you spend your coins to offer liquidity rather than keeping them in your account, they lose some of their worth. Additionally, between the time an order was issued and the moment it was completed, the asset value may change. Pricing instability is the term for this.
Both are good ways to create an extra income stream for yourself. Users should research the project and then invest.
You must understand the idea of irreversible damage if you offer money to an AMM. In other words, when you provide money to an AMM, you lose money in comparison to HODLing.

Risks of Liquidation Pools
You are likely susceptible to temporary loss if you provide cash to an AMM. If you're thinking about investing in a two-sided liquidity pool, be sure to read our article on it.
Smart contract vulnerabilities are another important consideration. A liquidity pool's assets become part of the pool whenever they are deposited. Therefore, even if there aren't any intermediaries physically keeping your money, you can think of the contract as acting as the money's guardian.
Additionally, be aware of developments in which the pool's regulations can be changed at the programmers' discretion. Devs can occasionally have direct access to the smart contract program, such as an administrator password. They may be able to use this to carry out possibly hazardous actions, such as gaining control of the pool's money.
One of the key technologies underlying the present DeFi software system is liquidity pools. They make possible decentralized lending, yield creation, exchange, and much more. Nearly every aspect of DeFi is powered by these smart contracts, and this is most likely to remain the case.